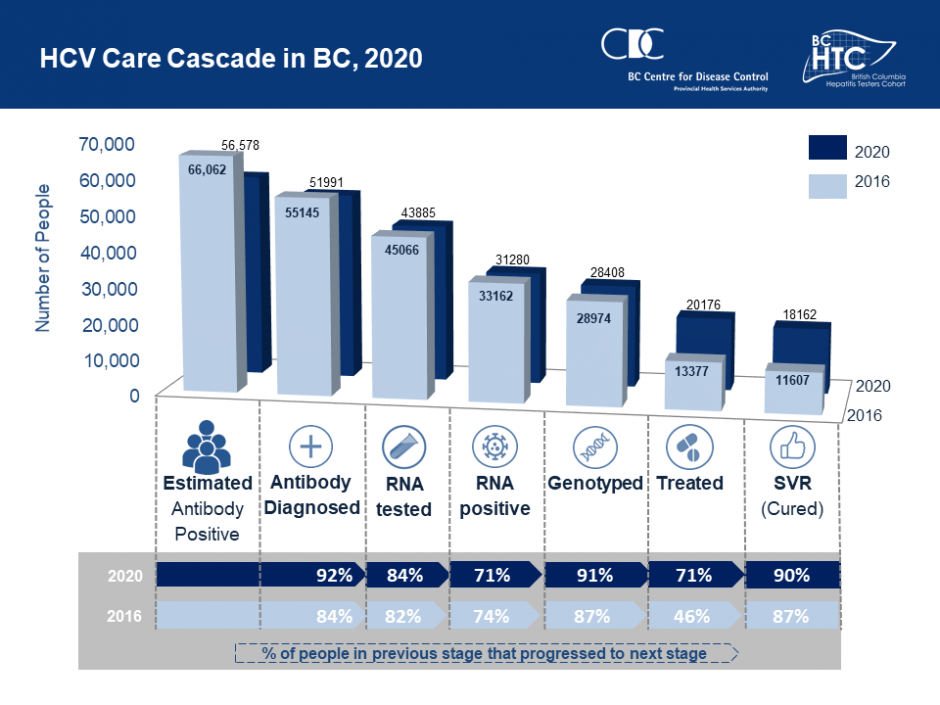
- Integration of various data sources enables HCV monitoring across the care cascade to assess program effectiveness.
- The majority of anti-HCV positive individuals were tested for RNA and genotyping.
- Very small proportion of HCV infected individuals received treatment.
- People with HIV coinfection and drug use despite being in liver care were less likely to receive treatment.
Also see: Bartlett, SR, Yu, A, Chapinal, N, et al. The population level care cascade for hepatitis C in British Columbia, Canada as of 2018: Impact of direct acting antivirals. Liver Int. 2019; 39: 2261– 2272. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14227
For 2012 Cascade, see paper published in EBioMedicine.
Citation: Janjua NZ, Kuo M, Yu A, Alvarez M, Wong S, Cook D, Wong J, Grebely J, Butt ZA, Samji H, Ramji A, Tyndall MW, Krajden M. The Population Level Cascade of Care for Hepatitis C in British Columbia, Canada: The BC Hepatitis Testers Cohort (BC-HTC). EBioMedicine 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.08.035